dx.doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2017.112
Preview meta tags from the dx.doi.org website.
Linked Hostnames
35- 37 links toscholar.google.com
- 35 links todx.doi.org
- 31 links todoi.org
- 26 links towww.nature.com
- 8 links towww.springernature.com
- 4 links topartnerships.nature.com
- 3 links toauthorservices.springernature.com
- 3 links toscholar.google.co.uk
Thumbnail
Search Engine Appearance
Data-driven planning of distributed energy resources amidst socio-technical complexities - Nature Energy
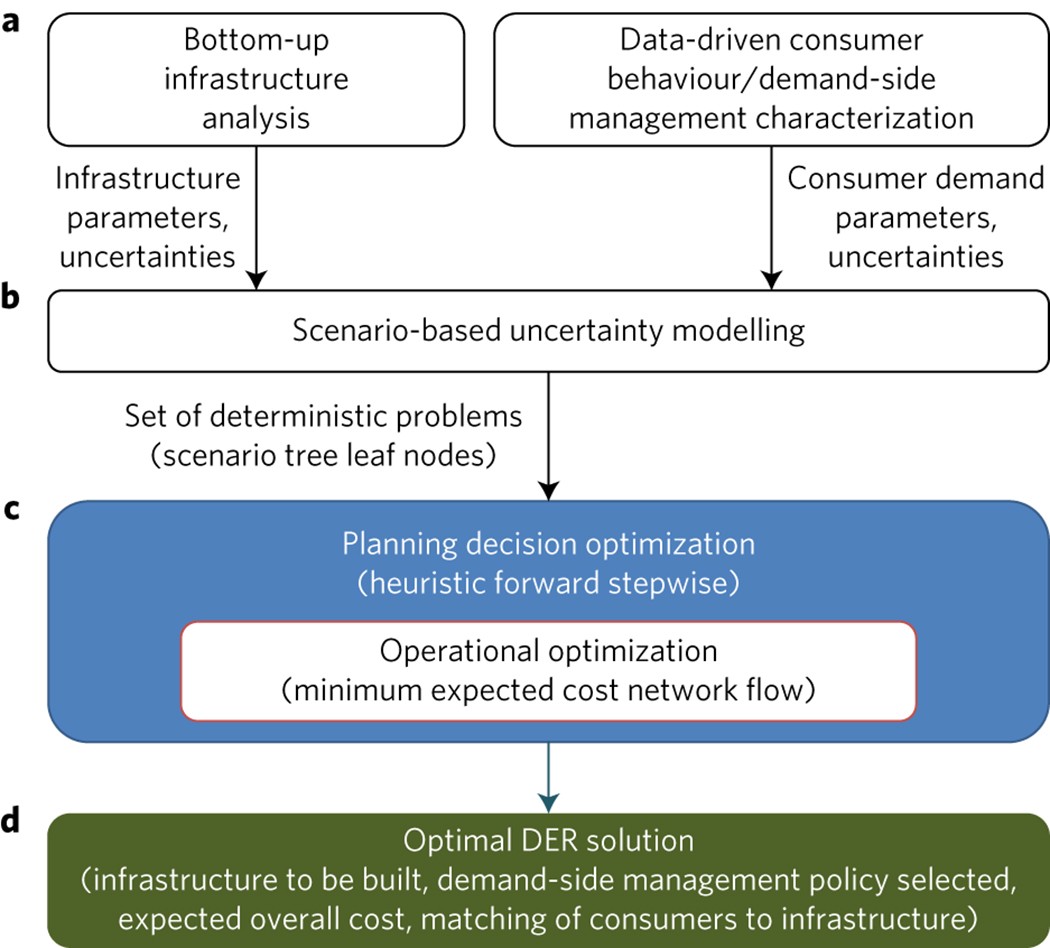
New distributed energy resources (DER) are rapidly replacing centralized power generation due to their environmental, economic and resiliency benefits. Previous analyses of DER systems have been limited in their ability to account for socio-technical complexities, such as intermittent supply, heterogeneous demand and balance-of-system cost dynamics. Here we develop ReMatch, an interdisciplinary modelling framework, spanning engineering, consumer behaviour and data science, and apply it to 10,000 consumers in California, USA. Our results show that deploying DER would yield nearly a 50% reduction in the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) over the status quo even after accounting for socio-technical complexities. We abstract a detailed matching of consumers to DER infrastructure from our results and discuss how this matching can facilitate the development of smart and targeted renewable energy policies, programmes and incentives. Our findings point to the large-scale economic and technical feasibility of DER and underscore the pertinent role DER can play in achieving sustainable energy goals. Planning of distributed energy resources requires careful consideration of many socio-technical factors to ensure that it is optimally built. Jain et al. present a model that incorporates numerous such factors and use it to find cost-effective resources for a sample of 10,000 consumers in California.
Bing
Data-driven planning of distributed energy resources amidst socio-technical complexities - Nature Energy
New distributed energy resources (DER) are rapidly replacing centralized power generation due to their environmental, economic and resiliency benefits. Previous analyses of DER systems have been limited in their ability to account for socio-technical complexities, such as intermittent supply, heterogeneous demand and balance-of-system cost dynamics. Here we develop ReMatch, an interdisciplinary modelling framework, spanning engineering, consumer behaviour and data science, and apply it to 10,000 consumers in California, USA. Our results show that deploying DER would yield nearly a 50% reduction in the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) over the status quo even after accounting for socio-technical complexities. We abstract a detailed matching of consumers to DER infrastructure from our results and discuss how this matching can facilitate the development of smart and targeted renewable energy policies, programmes and incentives. Our findings point to the large-scale economic and technical feasibility of DER and underscore the pertinent role DER can play in achieving sustainable energy goals. Planning of distributed energy resources requires careful consideration of many socio-technical factors to ensure that it is optimally built. Jain et al. present a model that incorporates numerous such factors and use it to find cost-effective resources for a sample of 10,000 consumers in California.
DuckDuckGo
Data-driven planning of distributed energy resources amidst socio-technical complexities - Nature Energy
New distributed energy resources (DER) are rapidly replacing centralized power generation due to their environmental, economic and resiliency benefits. Previous analyses of DER systems have been limited in their ability to account for socio-technical complexities, such as intermittent supply, heterogeneous demand and balance-of-system cost dynamics. Here we develop ReMatch, an interdisciplinary modelling framework, spanning engineering, consumer behaviour and data science, and apply it to 10,000 consumers in California, USA. Our results show that deploying DER would yield nearly a 50% reduction in the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) over the status quo even after accounting for socio-technical complexities. We abstract a detailed matching of consumers to DER infrastructure from our results and discuss how this matching can facilitate the development of smart and targeted renewable energy policies, programmes and incentives. Our findings point to the large-scale economic and technical feasibility of DER and underscore the pertinent role DER can play in achieving sustainable energy goals. Planning of distributed energy resources requires careful consideration of many socio-technical factors to ensure that it is optimally built. Jain et al. present a model that incorporates numerous such factors and use it to find cost-effective resources for a sample of 10,000 consumers in California.
General Meta Tags
111- titleData-driven planning of distributed energy resources amidst socio-technical complexities | Nature Energy
- titleClose banner
- titleClose banner
- X-UA-CompatibleIE=edge
- applicable-devicepc,mobile
Open Graph Meta Tags
6- og:urlhttps://www.nature.com/articles/nenergy2017112
- og:typearticle
- og:site_nameNature
- og:titleData-driven planning of distributed energy resources amidst socio-technical complexities - Nature Energy
- og:descriptionPlanning of distributed energy resources requires careful consideration of many socio-technical factors to ensure that it is optimally built. Jain et al. present a model that incorporates numerous such factors and use it to find cost-effective resources for a sample of 10,000 consumers in California.
Twitter Meta Tags
6- twitter:site@NatureEnergyJnl
- twitter:cardsummary_large_image
- twitter:image:altContent cover image
- twitter:titleData-driven planning of distributed energy resources amidst socio-technical complexities
- twitter:descriptionNature Energy - Planning of distributed energy resources requires careful consideration of many socio-technical factors to ensure that it is optimally built. Jain et al. present a model that...
Item Prop Meta Tags
5- position1
- position2
- position3
- position4
- publisherSpringer Nature
Link Tags
15- alternatehttps://www.nature.com/nenergy.rss
- apple-touch-icon/static/images/favicons/nature/apple-touch-icon-f39cb19454.png
- canonicalhttps://www.nature.com/articles/nenergy2017112
- icon/static/images/favicons/nature/favicon-48x48-b52890008c.png
- icon/static/images/favicons/nature/favicon-32x32-3fe59ece92.png
Emails
2Links
181- http://insideevs.com/solarcity-reveals-installed-pricing-for-tesla-powerwall
- http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=A%20fuzzy%20environmental-technical-economic%20model%20for%20distributed%20generation%20planning&journal=Energy&doi=10.1016%2Fj.energy.2011.03.048&volume=36&pages=3437-3445&publication_year=2011&author=Zangeneh%2CA&author=Jadid%2CS&author=Rahimi-Kian%2CA
- http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=A%20new%20approach%20for%C2%A0optimum%20simultaneous%20multi-DG%20distributed%20generation%20Units%20placement%C2%A0and%20sizing%20based%20on%20maximization%20of%20system%20loadability%20using%20HPSO%C2%A0%28hybrid%20particle%20swarm%20optimization%29%20algorithm&journal=Energy&doi=10.1016%2Fj.energy.2013.12.037&volume=66&pages=202-215&publication_year=2014&author=Aman%2CMM&author=Jasmon%2CGB&author=Bakar%2CaHa&author=Mokhlis%2CH
- http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=A%20review%20of%20solar%20photovoltaic%C2%A0levelized%20cost%20of%20electricity&journal=Renew.%20Sustain.%20Energy%20Rev.&doi=10.1016%2Fj.rser.2011.07.104&volume=15&pages=4470-4482&publication_year=2011&author=Branker%2CK&author=Pathak%2CMJM&author=Pearce%2CJM
- http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=A%20risk-based%20simulation%20and%20multi-objective%20optimization%20framework%20for%20the%20integration%20of%20distributed%20renewable%20generation%20and%20storage&journal=Renew.%20Sustain.%20Energy%20Rev.&doi=10.1016%2Fj.rser.2014.05.046&volume=37&pages=778-793&publication_year=2014&author=Mena%2CR&author=Hennebel%2CM&author=Li%2CY-F&author=Ruiz%2CC&author=Zio%2CE