doi.org/10.1039/D4MH00899E
Preview meta tags from the doi.org website.
Linked Hostnames
15- 27 links todoi.org
- 24 links towww.rsc.org
- 7 links toorcid.org
- 2 links tobooks.rsc.org
- 2 links tocreativecommons.org
- 2 links totwitter.com
- 1 link toblogs.rsc.org
- 1 link toedu.rsc.org
Thumbnail
Search Engine Appearance
Functionalization of monolithic MOF thin films with hydrocarbon chains to achieve superhydrophobic surfaces with tunable water adhesion strength
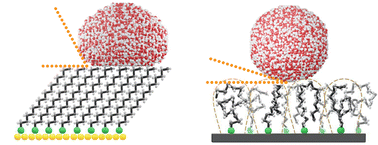
While the accessible pores render an enormous variety of functionalities to the bulk of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), the outer surfaces exposed by these crystalline materials also offer unique characteristics not available when using conventional substrates. By grafting hydrocarbon chains to well-defined
Bing
Functionalization of monolithic MOF thin films with hydrocarbon chains to achieve superhydrophobic surfaces with tunable water adhesion strength
While the accessible pores render an enormous variety of functionalities to the bulk of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), the outer surfaces exposed by these crystalline materials also offer unique characteristics not available when using conventional substrates. By grafting hydrocarbon chains to well-defined
DuckDuckGo
Functionalization of monolithic MOF thin films with hydrocarbon chains to achieve superhydrophobic surfaces with tunable water adhesion strength
While the accessible pores render an enormous variety of functionalities to the bulk of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), the outer surfaces exposed by these crystalline materials also offer unique characteristics not available when using conventional substrates. By grafting hydrocarbon chains to well-defined
General Meta Tags
131- titleFunctionalization of monolithic MOF thin films with hydrocarbon chains to achieve superhydrophobic surfaces with tunable water adhesion strength - Materials Horizons (RSC Publishing)
- charsetutf-8
- X-UA-CompatibleIE=edge
- viewportwidth=device-width, initial-scale=1
- format-detectiontelephone=no
Open Graph Meta Tags
5- og:urlhttps://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2025/mh/d4mh00899e
- og:typeArticle
- og:titleFunctionalization of monolithic MOF thin films with hydrocarbon chains to achieve superhydrophobic surfaces with tunable water adhesion strength
- og:imagehttps://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/Image/GA/D4MH00899E
- og:descriptionWhile the accessible pores render an enormous variety of functionalities to the bulk of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), the outer surfaces exposed by these crystalline materials also offer unique characteristics not available when using conventional substrates. By grafting hydrocarbon chains to well-defined
Twitter Meta Tags
2- twitter:cardsummary_large_image
- twitter:site@MaterHoriz
Link Tags
11- apple-touch-icon/apple-touch-icon.png
- canonicalhttps://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2025/mh/d4mh00899e
- dns-prefetch//www.rsc-cdn.org
- dns-prefetch//www.googletagmanager.com
- dns-prefetch//www.google-analytics.com
Emails
1Links
73- http://blogs.rsc.org
- http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
- http://pubs.rsc.org/historical-collection
- http://www.chemspider.com
- https://books.rsc.org/books/collections/series